With human blood cell typing pogil answers at the forefront, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of blood typing, empowering individuals with a profound understanding of this vital medical procedure. By exploring the different blood types, antigens, and inheritance patterns, readers will gain invaluable knowledge that extends beyond the classroom and into real-world applications.
This guide will navigate through the complexities of the ABO and Rh blood group systems, shedding light on their clinical significance and the techniques employed for accurate blood cell typing. Furthermore, it will delve into the practical applications of blood typing in medicine, forensics, and genetic research, highlighting its indispensable role in ensuring safe transfusions, organ transplants, and resolving paternity disputes.
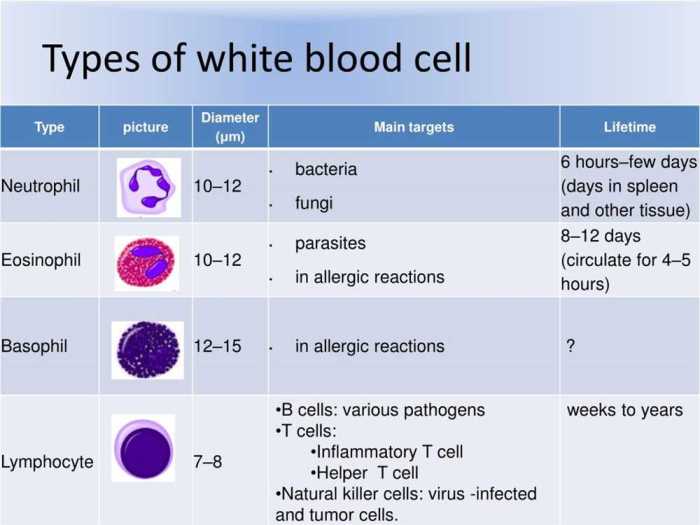
Blood Typing Overview

Blood typing is a crucial medical procedure that determines an individual’s blood type based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of their red blood cells. This information plays a vital role in blood transfusions, organ transplants, and various medical procedures to ensure compatibility and prevent adverse reactions.
The most common blood typing system, known as the ABO system, categorizes blood into four main types: A, B, AB, and O. Each blood type is characterized by the presence or absence of two antigens, A and B, on the surface of red blood cells.
Individuals with type A blood have only A antigens, those with type B blood have only B antigens, those with type AB blood have both A and B antigens, and those with type O blood have neither A nor B antigens.
Blood Typing Process
Blood typing involves a series of tests that analyze the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. The most common method is the slide agglutination test, which involves mixing a sample of the patient’s blood with antisera containing known antibodies against A and B antigens.
If agglutination, or clumping, occurs, it indicates the presence of the corresponding antigen on the patient’s red blood cells.
ABO Blood Group System
The ABO blood group system is one of the most important blood group systems in humans. It is determined by the presence or absence of two antigens, A and B, on the surface of red blood cells. There are four main blood types in the ABO system: A, B, AB, and O.The
inheritance of ABO blood types is determined by three alleles: A, B, and O. The A and B alleles are dominant, while the O allele is recessive. A person who inherits two A alleles will have blood type A, a person who inherits two B alleles will have blood type B, a person who inherits one A allele and one B allele will have blood type AB, and a person who inherits two O alleles will have blood type O.The
ABO blood group system is important because it can affect the compatibility of blood transfusions. A person can only receive a blood transfusion from someone who has the same blood type or a compatible blood type. For example, a person with blood type A can only receive blood from someone with blood type A or O.
Rh Blood Group System
The Rh blood group system is a complex system of antigens found on the surface of red blood cells. The most important Rh antigen is the D antigen, which is present in approximately 85% of the population and is responsible for the Rh-positive blood type.
People who lack the D antigen are Rh-negative.
The Rh blood group system is inherited in a Mendelian fashion, with the D antigen being dominant over the d antigen. This means that a person who inherits one D allele and one d allele will be Rh-positive, while a person who inherits two d alleles will be Rh-negative.
Clinical Significance of Rh Incompatibility
Rh incompatibility can occur when an Rh-negative mother carries an Rh-positive fetus. During pregnancy, the mother’s immune system can recognize the Rh antigen on the fetal red blood cells as foreign and produce antibodies against it. These antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the fetal red blood cells, causing a condition called erythroblastosis fetalis.
Erythroblastosis fetalis can lead to a number of serious complications, including anemia, jaundice, and heart failure. In severe cases, it can even be fatal.
Rh incompatibility can be prevented by administering Rh immune globulin (RhIg) to Rh-negative mothers. RhIg is a medication that contains antibodies against the Rh antigen. When given to an Rh-negative mother, RhIg binds to any Rh-positive fetal red blood cells that may have crossed the placenta and prevents the mother’s immune system from attacking them.
Human Blood Cell Typing Techniques
Blood cell typing is a laboratory procedure used to determine the type of antigens present on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). This information is crucial for safe blood transfusions, as it helps prevent transfusion reactions and other complications.
Various techniques are employed for human blood cell typing, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Slide Agglutination Test
The slide agglutination test is a simple and rapid method for blood cell typing. It involves mixing a drop of blood with antisera containing antibodies against specific antigens on the RBC surface. If agglutination (clumping) occurs, it indicates the presence of the corresponding antigen on the RBCs.
Advantages:
- Simple and easy to perform
- Rapid results
- Low cost
Disadvantages:
- Can be subjective in interpretation
- Not as sensitive as other methods
- Limited number of antigens that can be tested simultaneously
Tube Agglutination Test, Human blood cell typing pogil answers
The tube agglutination test is a more sensitive and specific method compared to the slide agglutination test. It involves incubating a sample of blood with antisera in a test tube. The presence of agglutination is then observed visually or using a centrifuge.
Advantages:
- More sensitive and specific than the slide agglutination test
- Allows for the testing of a wider range of antigens
Disadvantages:
- More time-consuming than the slide agglutination test
- Requires specialized equipment and training
Gel Card Technology
Gel card technology is a newer method for blood cell typing that utilizes a gel card with immobilized antibodies. A drop of blood is added to the card, and the antibodies in the gel interact with the corresponding antigens on the RBCs.
The results are visualized as colored spots on the card.
Advantages:
- Automated and standardized
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Allows for the simultaneous testing of multiple antigens
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than traditional methods
- Requires specialized equipment and training
Molecular Techniques
Molecular techniques, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and DNA sequencing, can also be used for blood cell typing. These techniques analyze the DNA of the RBCs to determine the presence of specific genes responsible for antigen expression.
Advantages:
- Highly specific and sensitive
- Can identify rare antigens and mutations
Disadvantages:
- Complex and time-consuming
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise
Quality Control Measures
Quality control measures are essential in blood cell typing to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. These measures include:
- Regular calibration and maintenance of equipment
- Use of standardized reagents and procedures
- Internal and external quality control programs
- Training and certification of laboratory personnel
Applications of Blood Typing
Blood typing plays a crucial role in various medical and scientific fields. Its applications extend beyond transfusion and organ transplantation, providing valuable insights in forensics, paternity determination, population studies, and genetic research.
Transfusion and Organ Transplantation
Blood typing is essential in ensuring the compatibility of blood transfusions and organ transplants. By matching the blood types of donors and recipients, medical professionals can prevent life-threatening reactions. For instance, a patient with type A blood can only receive blood from type A or O donors, while a patient with type B blood can receive blood from type B or O donors.
Forensic Science
Blood typing is a powerful tool in forensic science, assisting in the identification of suspects and victims. By analyzing blood samples found at crime scenes, investigators can determine the blood type of the individuals involved. This information can help narrow down the pool of suspects or identify the victim if their identity is unknown.
Paternity and Maternity Determination
Blood typing is a valuable method for establishing paternity or maternity. By comparing the blood types of the child and alleged parents, it is possible to determine whether the alleged parents could have biologically produced the child. While blood typing alone cannot conclusively prove paternity or maternity, it can provide strong evidence in support or against a claim.
Population Studies and Genetic Research
Blood typing contributes to population studies and genetic research by providing insights into the distribution of blood groups within different populations. By analyzing blood type frequencies, researchers can study population migrations, genetic diversity, and the prevalence of certain genetic disorders.
Blood Typing Practice Problems: Human Blood Cell Typing Pogil Answers
Practice problems involving blood typing scenarios provide an opportunity to apply the concepts and techniques learned in this lesson. By working through these problems, you can reinforce your understanding and gain confidence in your ability to determine blood types.
When solving blood typing problems, it is important to follow a logical and systematic approach. First, determine the known blood types of the individuals involved in the scenario. Next, use the rules of blood type inheritance to predict the possible blood types of the offspring or other individuals in the scenario.
Finally, compare your predictions to any additional information provided in the problem to determine the most likely blood types.
ABO Blood Group System
- A person with blood type A has the A antigen on their red blood cells. They can receive blood from people with blood types A or O, but not from people with blood types B or AB.
- A person with blood type B has the B antigen on their red blood cells. They can receive blood from people with blood types B or O, but not from people with blood types A or AB.
- A person with blood type AB has both the A and B antigens on their red blood cells. They can receive blood from people with any blood type.
- A person with blood type O has neither the A nor the B antigen on their red blood cells. They can only receive blood from people with blood type O.
Rh Blood Group System
- The Rh factor is a protein found on the surface of red blood cells. People who have the Rh factor are Rh-positive, while those who do not have the Rh factor are Rh-negative.
- Rh-positive people can receive blood from both Rh-positive and Rh-negative people. Rh-negative people can only receive blood from Rh-negative people.
FAQs
What is the purpose of blood typing?
Blood typing determines the compatibility of blood between individuals, ensuring safe transfusions and organ transplants.
What are the different blood types?
The main blood types are A, B, AB, and O, determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells.
How is blood typing performed?
Blood typing involves mixing a sample of blood with antibodies to identify the presence or absence of specific antigens.
What is the clinical significance of Rh incompatibility?
Rh incompatibility occurs when a Rh-negative mother carries a Rh-positive fetus, potentially leading to hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What are the applications of blood typing beyond medicine?
Blood typing is used in forensics to identify individuals, determine paternity, and study population genetics.