Chapter 10 anatomy and physiology answer key – Embark on a comprehensive journey through the intricate world of human anatomy and physiology with our exclusive Chapter 10 Answer Key. This definitive resource provides a wealth of insights into the structure and function of the human body, empowering you with a deeper understanding of its complexities.
Delve into the fascinating realms of skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, immune, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems, unraveling their intricate mechanisms and vital roles in maintaining human life.
Introduction

Anatomyis the study of the structure of the body, while physiologyis the study of how the body functions. Together, anatomy and physiology provide a comprehensive understanding of the human body and its workings.
Understanding anatomy and physiology is essential for healthcare professionals, as it forms the foundation for diagnosing and treating medical conditions. It is also important for individuals who want to maintain their health and well-being.
Organization of the Human Body

The human body is organized into a hierarchy of structural levels, from the smallest to the largest:
- Chemical level:Atoms, molecules, and ions
- Cellular level:Cells, the basic unit of life
- Tissue level:Groups of similar cells that perform a specific function
- Organ level:Structures composed of different tissues that perform a specific function
- Organ system level:Groups of organs that work together to perform a specific function
- Organismal level:The entire living body
The human body also has two major body cavities: the thoracic cavityand the abdominal cavity. The thoracic cavity contains the heart and lungs, while the abdominal cavity contains the stomach, intestines, and other digestive organs.
Integumentary System
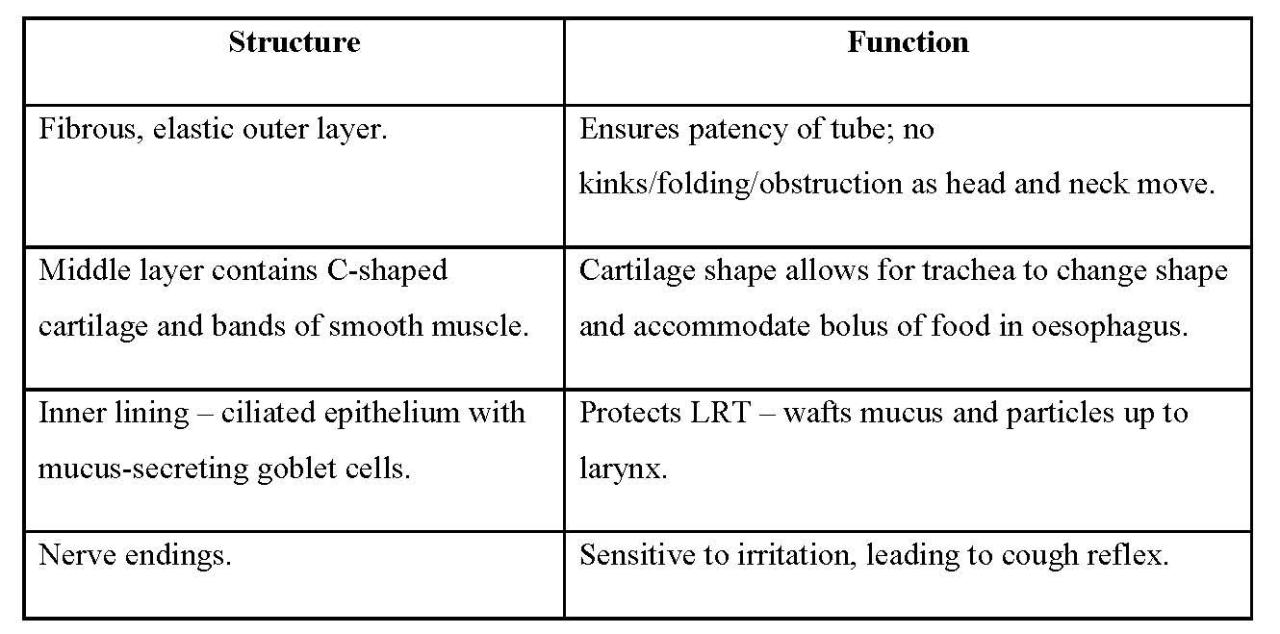
The integumentary system is the body’s outer covering, which consists of the skin, hair, and nails.
The skin has several important functions, including:
- Protection from the environment
- Regulation of body temperature
- Sensation
- Vitamin D synthesis
The skin is composed of three layers:
- Epidermis:The outermost layer, which is composed of keratinized cells
- Dermis:The middle layer, which is composed of connective tissue and blood vessels
- Hypodermis:The innermost layer, which is composed of adipose tissue
Skeletal System
The skeletal system is the body’s framework, which provides support, protection, and movement.
The skeletal system consists of 206 bones, which are classified into five types:
- Long bones:Found in the limbs
- Short bones:Found in the wrists and ankles
- Flat bones:Found in the skull and rib cage
- Irregular bones:Found in the vertebrae and facial bones
- Sesamoid bones:Small bones found in tendons
Bones are composed of a hard outer layer of compact bone and a softer inner layer of cancellous bone. Bones are also lined with a thin layer of cartilage called periosteum.
Expert Answers: Chapter 10 Anatomy And Physiology Answer Key
What is the significance of understanding anatomy and physiology?
Comprehending anatomy and physiology is crucial for various reasons. It provides a foundation for comprehending human health, disease, and treatment. It also enhances our appreciation for the complexity and resilience of the human body.
How is the human body organized structurally?
The human body exhibits a hierarchical organization, ranging from atoms to molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and ultimately the entire organism. This organization allows for specialized functions and efficient coordination.
What are the major body cavities?
The human body consists of two major body cavities: the dorsal cavity and the ventral cavity. The dorsal cavity is further divided into the cranial cavity and the spinal cavity, while the ventral cavity is divided into the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity.