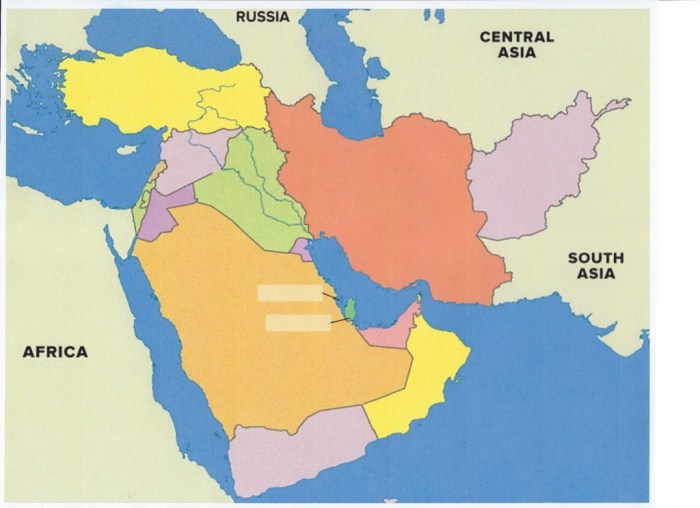
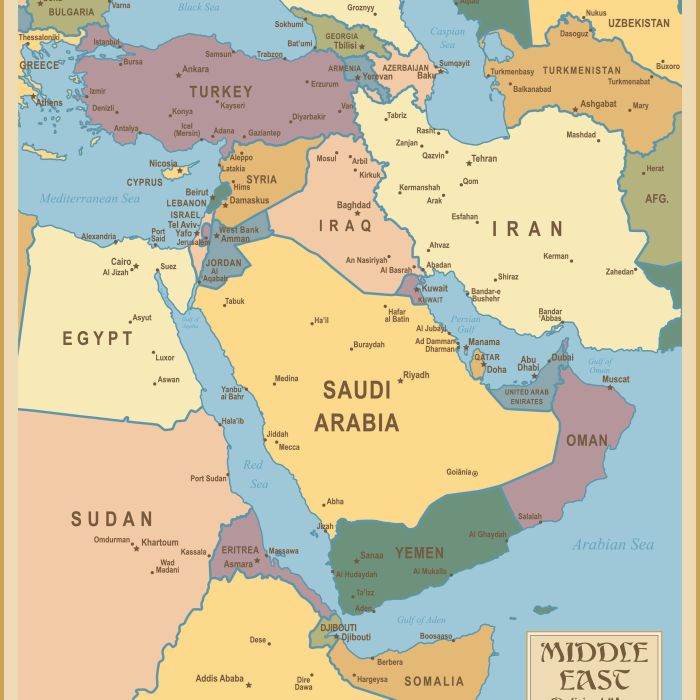
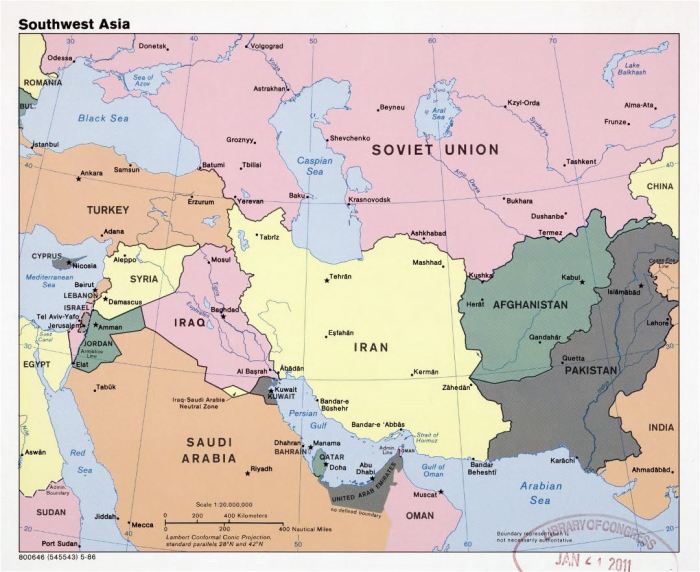
Unveiling the map of southwest asia labeled, this comprehensive guide embarks on an enthralling journey through the region’s diverse landscapes, rich history, and complex political dynamics. From the towering mountains to the vast deserts, this labeled map serves as an indispensable tool for understanding the intricacies of Southwest Asia.
As we delve into the heart of this captivating region, we’ll explore the physical and cultural contours that shape its identity, unravel the political boundaries that divide and connect its nations, and uncover the economic forces that drive its development.
Geographic Regions of Southwest Asia
Southwest Asia is a diverse region with a complex and fascinating geography. The region can be divided into several distinct geographic regions, each with its own unique physical and climatic characteristics.
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula is a vast and arid region that occupies the southernmost part of Southwest Asia. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west, the Arabian Sea to the south, and the Persian Gulf to the east.
The peninsula is home to some of the world’s largest deserts, including the Rub’ al Khali and the Great Nefud. The climate of the Arabian Peninsula is hot and dry, with little rainfall.
Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent is a region of Southwest Asia that is located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The region is home to some of the world’s oldest civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. The Fertile Crescent is a relatively fertile region, with a climate that is more temperate than the Arabian Peninsula.
Anatolian Plateau
The Anatolian Plateau is a region of Southwest Asia that is located in the central part of Turkey. The region is home to some of the world’s highest mountains, including Mount Ararat. The climate of the Anatolian Plateau is continental, with hot summers and cold winters.
Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains are a mountain range that is located between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. The range forms the border between Europe and Asia. The Caucasus Mountains are home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Elbrus.
The climate of the Caucasus Mountains is varied, with a range of temperatures and precipitation.
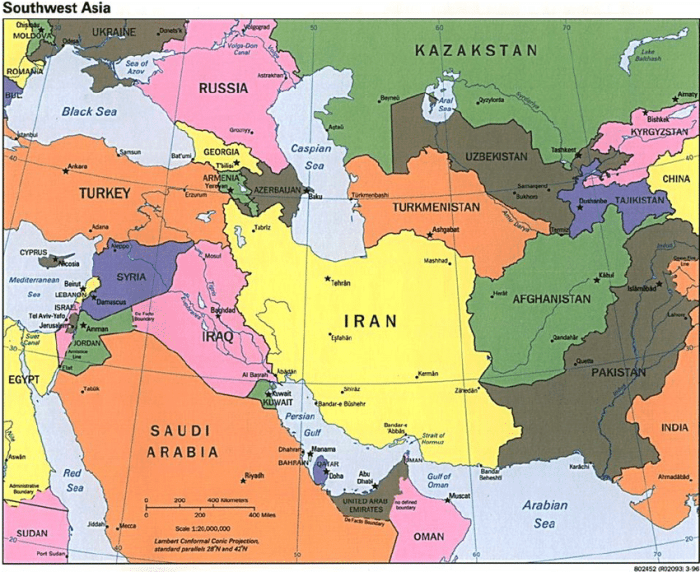
Political Boundaries and Countries
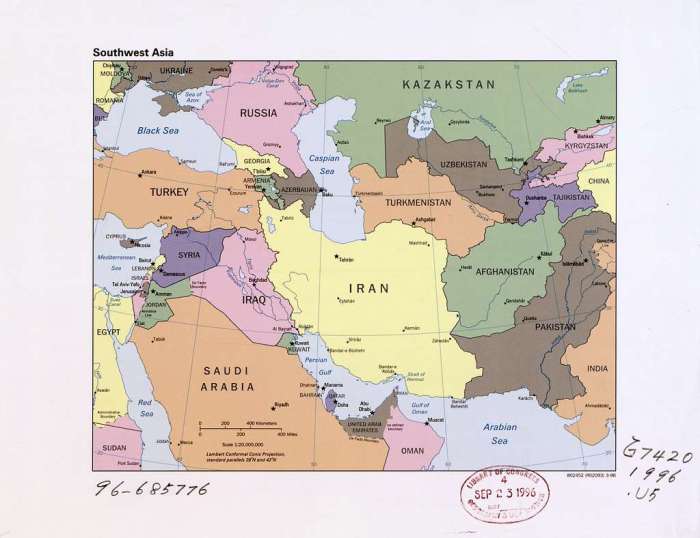
The political landscape of Southwest Asia is a complex and ever-changing tapestry. The region is home to a diverse array of countries, each with its unique history, culture, and political system.
Political Boundaries
The political boundaries of Southwest Asia have been shaped by centuries of conflict and conquest. The region has been ruled by a succession of empires, including the Persian, Greek, Roman, Arab, Ottoman, and British. Each empire has left its mark on the region’s political geography.
Today, Southwest Asia is divided into 18 countries. The largest country in the region is Saudi Arabia, which occupies the vast Arabian Peninsula. The smallest country is Bahrain, which is an archipelago located in the Persian Gulf.
Countries of Southwest Asia
| Country | Capital | Major Cities |
|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Kabul | Kandahar, Herat, Mazar-i-Sharif |
| Bahrain | Manama | Muharraq, Isa Town, Sitra |
| Cyprus | Nicosia | Limassol, Larnaca, Paphos |
| Egypt | Cairo | Alexandria, Giza, Luxor |
| Iran | Tehran | Mashhad, Isfahan, Tabriz |
| Iraq | Baghdad | Basra, Mosul, Erbil |
| Israel | Jerusalem | Tel Aviv, Haifa, Beersheba |
| Jordan | Amman | Zarqa, Irbid, Aqaba |
| Kuwait | Kuwait City | Hawalli, Salmiya, Farwaniya |
| Lebanon | Beirut | Tripoli, Sidon, Tyre |
| Oman | Muscat | Salalah, Sohar, Nizwa |
| Pakistan | Islamabad | Karachi, Lahore, Faisalabad |
| Palestine | Ramallah | Gaza City, Nablus, Jenin |
| Qatar | Doha | Al Rayyan, Umm Salal, Al Wakrah |
| Saudi Arabia | Riyadh | Jeddah, Mecca, Medina |
| Syria | Damascus | Aleppo, Homs, Hama |
| Turkey | Ankara | Istanbul, Izmir, Bursa |
| United Arab Emirates | Abu Dhabi | Dubai, Sharjah, Al Ain |
| Yemen | Sana’a | Aden, Ta’izz, Hodeidah |
Territorial Disputes and Political Conflicts
The political landscape of Southwest Asia is further complicated by a number of territorial disputes and political conflicts. These disputes have their roots in a variety of factors, including historical grievances, ethnic tensions, and religious differences.
Some of the most significant territorial disputes in the region include the Arab-Israeli conflict, the Kashmir conflict, and the Cyprus dispute. These disputes have led to a number of wars and other conflicts, and they continue to be a source of tension in the region.
Historical Landmarks and Cultural Heritage
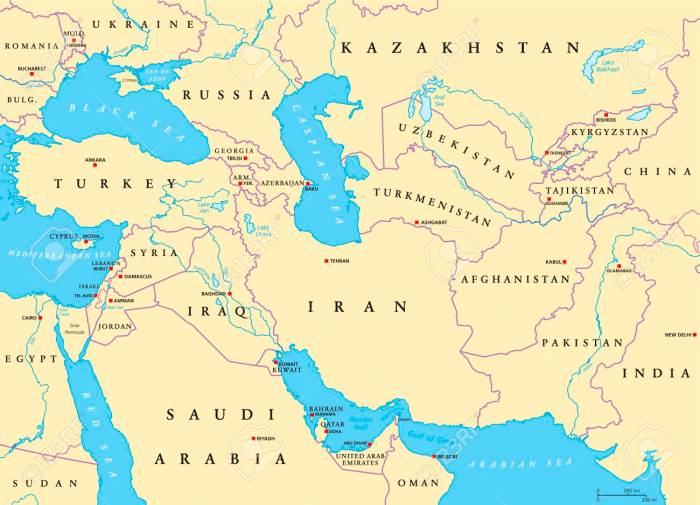
Southwest Asia boasts a rich tapestry of historical landmarks and cultural heritage sites that have shaped the region’s identity and legacy. These landmarks bear witness to the civilizations that have flourished in this region, leaving behind a legacy of architectural marvels, religious monuments, and cultural traditions that continue to inspire and captivate visitors today.
Ancient Cities
The ruins of ancient cities, such as Petra in Jordan and Palmyra in Syria, offer a glimpse into the grandeur of bygone eras. Petra, carved into the sheer rock face of the Jordanian desert, was once a thriving metropolis of the Nabatean kingdom.
Its elaborate facades, intricate carvings, and sophisticated water management system showcase the architectural prowess of its builders.
Palmyra, once a prosperous trading hub on the Silk Road, boasts monumental temples, colonnaded streets, and an impressive amphitheater. Its ruins stand as a testament to the cultural exchange and architectural achievements of the Roman Empire.
Religious Monuments
Southwest Asia is home to some of the world’s most sacred religious sites. The Al-Masjid al-Haram in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, is the holiest site in Islam and attracts millions of pilgrims annually. Its central structure, the Kaaba, is believed to have been built by the Prophet Muhammad and is a focal point for Muslim prayers.
The Western Wall in Jerusalem is a remnant of the Second Temple, one of the holiest sites in Judaism. It is a place of prayer and pilgrimage for Jews around the world.
Cultural Traditions
The cultural heritage of Southwest Asia extends beyond its historical landmarks. The region is renowned for its vibrant music, dance, and culinary traditions. Traditional Bedouin music, with its distinctive rhythms and instruments, is a testament to the nomadic lifestyle of the region’s inhabitants.
Arabic coffee, with its rich aroma and bitter taste, is an integral part of social gatherings and hospitality in Southwest Asia. The preparation and serving of coffee is a ritualized process that reflects the cultural values of the region.
For those interested in the intricacies of map reading, the labeled map of Southwest Asia offers a comprehensive visual aid. For equestrian enthusiasts seeking guidance on equestrian skills, the dressage first level test 1 provides valuable insights. Returning to the topic of geography, the labeled map of Southwest Asia remains an invaluable tool for understanding the region’s geopolitical landscape.
Economic Activities and Resources: Map Of Southwest Asia Labeled
Southwest Asia is endowed with abundant natural resources and diverse economic activities. The region is renowned for its oil and gas production, which plays a pivotal role in global energy markets.
Oil and Gas Production
Southwest Asia is home to some of the world’s largest oil and gas reserves. The region’s oil-rich nations, such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Kuwait, are major exporters of crude oil and natural gas. Oil and gas production is the backbone of many Southwest Asian economies, providing significant revenues for governments and driving economic growth.
Agriculture
Despite its arid climate, Southwest Asia has a rich agricultural tradition. The region is a major producer of dates, citrus fruits, and vegetables. In recent years, modern irrigation techniques have expanded agricultural productivity, making the region more self-sufficient in food production.
Tourism
Tourism is a growing industry in Southwest Asia. The region boasts a rich cultural heritage, ancient historical sites, and natural wonders that attract tourists from around the world. Countries like Jordan, Egypt, and the United Arab Emirates have invested heavily in tourism infrastructure to capitalize on this growing sector.
Other Industries
In addition to oil and gas, agriculture, and tourism, Southwest Asia has a diversified industrial base. The region is home to a range of industries, including manufacturing, construction, and financial services. These industries contribute to economic diversification and create employment opportunities.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities, Map of southwest asia labeled
Southwest Asia faces both economic challenges and opportunities. The region’s reliance on oil and gas exports makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global energy prices. Diversifying economies, investing in renewable energy, and developing human capital are crucial for long-term economic sustainability.On
the other hand, Southwest Asia has the potential to become a major economic hub. Its strategic location at the crossroads of three continents offers opportunities for trade and investment. The region’s young and growing population provides a vast labor force that can drive economic growth.
By harnessing these opportunities and addressing the challenges, Southwest Asia can achieve sustainable economic development.
Infrastructure and Transportation
Infrastructure plays a crucial role in economic development and regional connectivity. Southwest Asia is home to major transportation networks that facilitate trade, travel, and communication.
Major Highways and Railways
The region boasts an extensive network of highways and railways connecting major cities and countries. The Trans-Arabian Highway, spanning over 5,000 kilometers, links the Arabian Peninsula with the Levant and Iraq. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Railway, currently under construction, aims to connect the GCC countries and enhance regional integration.
Airports and Seaports
Southwest Asia has several international airports, including Dubai International Airport, Hamad International Airport, and King Fahd International Airport. These airports serve as major hubs for regional and global air travel. Major seaports, such as Jebel Ali Port and Mina Salman, facilitate maritime trade and connect the region to the rest of the world.
Infrastructure Challenges
Despite significant infrastructure development, Southwest Asia faces challenges related to maintaining and expanding its transportation networks. Political instability, limited funding, and environmental concerns can hinder infrastructure projects. Additionally, the region’s vast desert terrain presents logistical challenges for transportation.
FAQ Corner
What is the largest country in Southwest Asia?
Saudi Arabia
What is the most populous country in Southwest Asia?
Iran
What is the major river that flows through Southwest Asia?
Tigris River
What is the highest mountain in Southwest Asia?
Mount Damavand
What is the main religion practiced in Southwest Asia?
Islam